5 minutes
Building SSHplex: More details
The Problem
At Kindred, we relied on Remote Desktop Manager (RDM) to manage connections to our Windows and Linux hosts. I primarily used it to connect to multiple VMs simultaneously and broadcast commands to check system states or run quick commands where Ansible ad-hoc was either too slow or when I needed immediate feedback.
However, we faced two major issues:
- Licensing costs: The license was expiring and renewal was expensive
- Maintenance overhead: Every new host had to be manually added to the RDM SQL Server database
After searching for alternatives, I found nothing that met our specific needs. So I decided to build my own solution.
Solution Design
I identified three core requirements for the new tool:
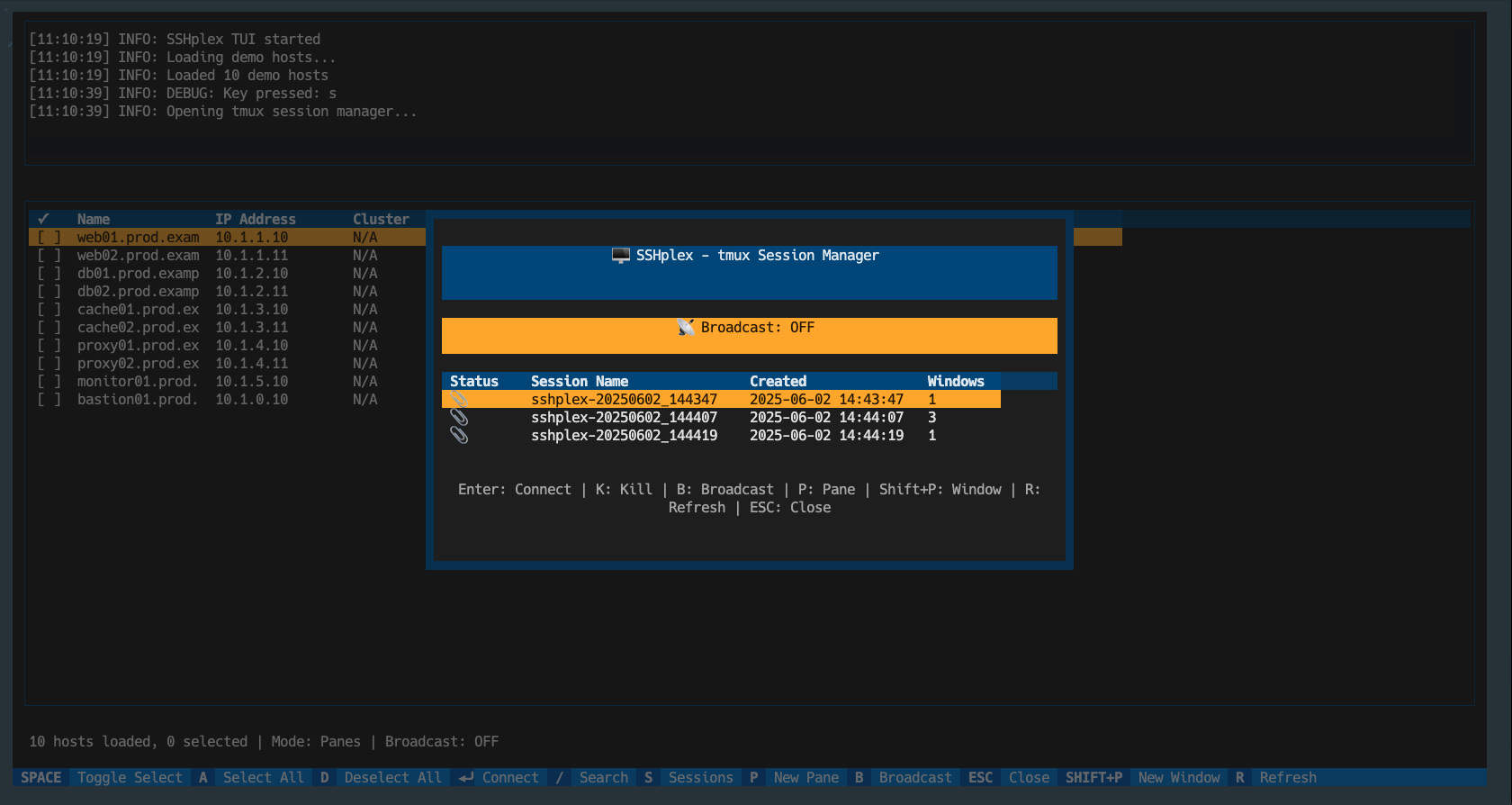
🖥️ Modern Terminal User Interface
- Host selection interface with search capabilities
- Bulk selection with hotkeys (like pressing ‘A’ to select all)
- Command broadcasting across multiple SSH sessions
🔗 Flexible Source of Truth Integration
- NetBox integration for VMs and devices
- Ansible inventory support with merging capabilities from multiple files
- Extensible architecture for future data sources
🖼️ Terminal Multiplexer Support
- tmux integration as the initial multiplexer (widely available with excellent Python libraries)
- Extensible design for future multiplexer support
- Session Keepalived sometimes i close my terminal but i want my background task to work and comming back to it
Development Approach
I followed the KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid) principle and broke development into three phases:
Phase 1: Foundation
- Configuration system with proper validation
- NetBox connectivity and VM listing
- Basic TUI for host selection
- Single SSH connection functionality
- Logging infrastructure with proper namespacing
Phase 2: Core Features
- Multi-select capability in the TUI
- tmux session management with multiple panes
- Connection error handling and retry logic
- Search and filtering functionality
Phase 3: Polish & Performance
- Command broadcasting between panes
- Session persistence and management
- Advanced error recovery mechanisms
- Performance optimization with intelligent caching
CI/CD
After having a first version i quickly needed a pipeline to test/lint my code and deploy it easily into github and pypi I created 2 pipeline:
- The first one was a ci based on PR trigger, to check for linting and basic test (demo mode in my app)
- The seccond one was for building and releasing the app based on tags, it uploads to github releases with a description based on commits and also release it to pypi for pip install
Implementation Strategy
I leveraged GitHub Copilot extensively during development, using structured prompts to maintain consistency and follow best practices. The modular approach allowed me to:
- Iterate quickly on each component
- Test incrementally as features were added
- Maintain clean separation between UI, data sources, and multiplexer logic
- Plan for extensibility from the start
This methodical approach ensured that SSHplex evolved from a simple concept into a robust tool that addresses real infrastructure management challenges.
CI/CD Pipeline
Building a reliable CI/CD pipeline was crucial for maintaining code quality and enabling rapid iteration:
🔄 Automated Testing & Quality
- GitHub Actions for continuous integration
- Pytest with comprehensive test coverage for core functionality
- Code quality checks using flake8 and mypi for consistent formatting
📦 Package Distribution
- PyPI publishing with automated versioning and release notes
- Multi-version testing across python versions
🚀 Release Strategy
- Semantic versioning with automated changelog generation
The pipeline reduced manual overhead significantly and caught integration issues early, allowing me to focus on feature development rather than release management.
Leveraging Large Language Models
My experience with LLMs during this project highlighted the importance of choosing the right tool for the task:
🔄 Evolution of AI Assistance
Initially, I started with Claude Sonnet 3.5, but encountered several limitations:
- Over-engineering: Often generated unnecessarily complex solutions
- Context misunderstanding: Frequently missed the specific requirements or intent
- Inconsistent results: Code quality varied significantly between iterations
When Anthropic announced Claude Sonnet 4 in preview (available in VS Code), the experience transformed completely:
- Precise execution: With clear instructions, it consistently delivered working Python code
- Agent mode debugging: Exceptional at identifying and fixing issues autonomously
- Intent understanding: Better grasp of project context and requirements
🎯 Strategic Implementation Approach
Rather than relying on random code suggestions, I developed a structured workflow:
Detailed Instruction Sets:
"Create a NetBox API client class with connection pooling, automatic retry logic
with exponential backoff, proper SSL certificate handling, and comprehensive
error handling for device and VM queries. Include logging and timeout management."
Iterative Refinement:
- Start with high-level architecture prompts
- Break down complex features into smaller, specific tasks
- Use the agent mode for debugging and optimization passes
💡 Key Success Areas
The LLM excelled particularly in:
- Boilerplate elimination - Configuration parsing and validation schemas
- API integration patterns - Consistent error handling across different data sources
- Test coverage generation - Comprehensive unit test scaffolding
- Code refactoring - Maintaining consistency across modules during iterations
⚖️ Human-AI Collaboration Balance
The most effective approach was treating the LLM as a highly skilled pair programmer:
- Architecture decisions remained human-driven
- Implementation details leveraged AI efficiency
- Domain expertise guided prompt engineering and validation
- Code review ensured real-world applicability
This collaboration model increased development velocity by approximately 40% while maintaining code quality and architectural integrity.
💡 Code Generation & Boilerplate
- Configuration parsing - Copilot excelled at generating YAML validation schemas
- API integration code - Particularly helpful for NetBox API client implementation
- Error handling patterns - Consistent exception handling across modules
- Test case generation - Automated creation of unit test scaffolding
🎯 Structured Prompting Strategy
Instead of random suggestions, I used specific prompts:
"Generate a NetBox API client class with connection pooling,
retry logic, and proper error handling for device queries"
"Create a tmux session manager that handles pane creation,
layout management, and graceful cleanup on session termination"
⚖️ Human Oversight & Validation
- Code review - All generated code underwent manual review
- Architecture decisions - LLM suggestions informed but didn’t dictate design choices
- Domain expertise - Combined AI efficiency with infrastructure knowledge
- Testing validation - Ensured generated code met real-world requirements
📈 Productivity Impact
Using LLMs strategically increased development velocity by approximately 30-40%, particularly in:
- Reducing boilerplate writing time
- Accelerating API integration development
- Generating comprehensive test coverage
- Maintaining consistent code patterns
The key was treating Copilot as a sophisticated autocomplete rather than an architect - keeping human judgment central to design decisions while leveraging AI for implementation efficiency.