2 minutes
Building SSHplex: A Modern TUI for SSH Connection Multiplexing
The Problem
At Kindred, we relied on Remote Desktop Manager (RDM) to manage connections to our Windows and Linux hosts for broadcasting commands and checking system states. However, licensing costs were high and every new host required manual database entry. After finding no suitable alternatives, I decided to build my own solution.
Solution Design
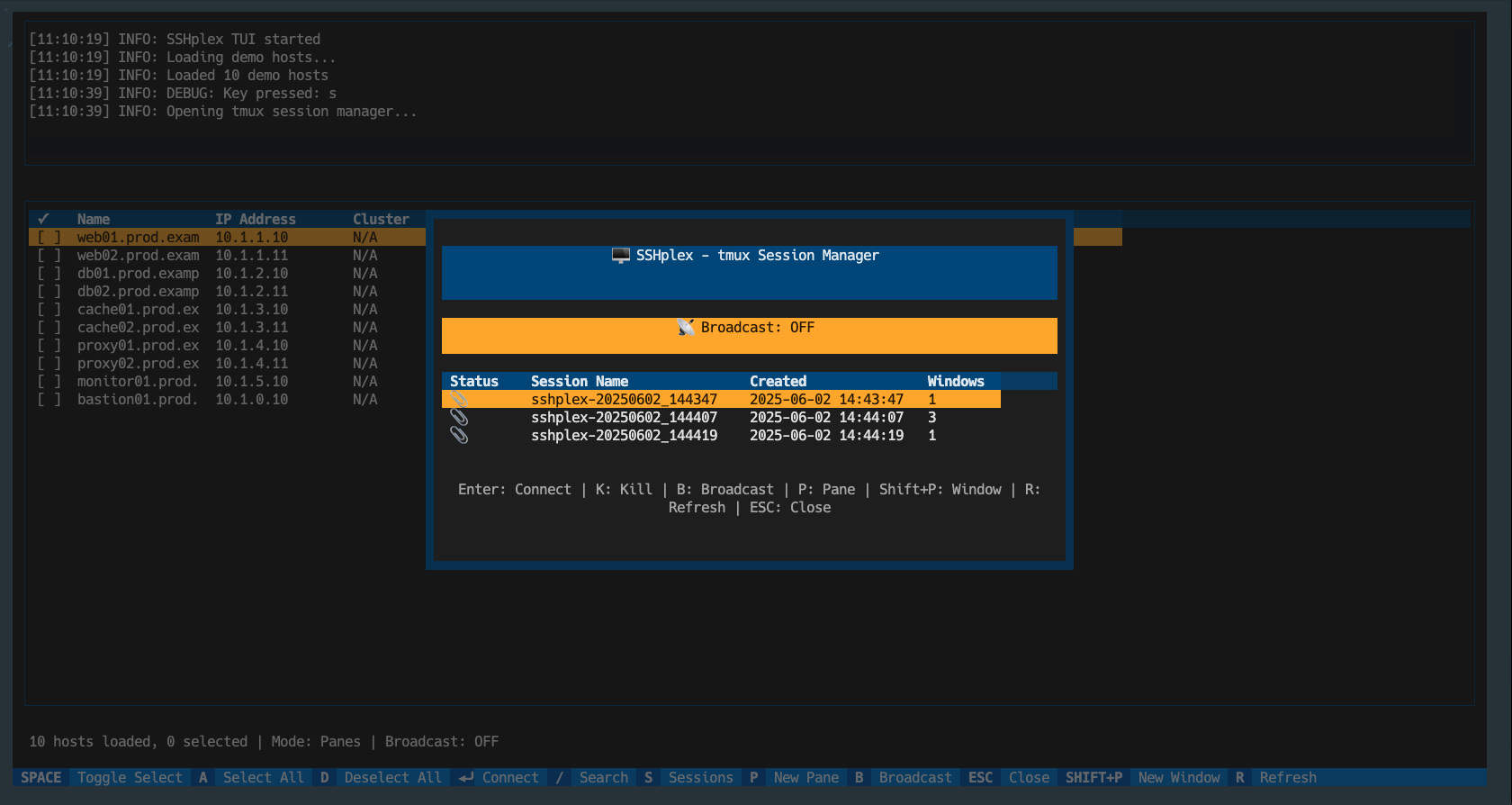
SSHplex needed three core capabilities: a modern terminal UI with host selection and bulk operations, flexible data source integration (NetBox and Ansible inventory), and terminal multiplexer support with session persistence for background tasks.
Development Approach
Following KISS principles, I structured development in three phases. First, building the foundation with configuration, NetBox connectivity, basic TUI, and single SSH connections. Second, adding multi-select functionality, tmux session management, and error handling. Finally, implementing command broadcasting, session persistence, and performance optimization.
The modular architecture allowed rapid iteration while maintaining clean separation between UI, data sources, and multiplexer logic. I implemented CI/CD early with two pipelines: PR-triggered testing and linting, plus tag-based releases to GitHub and PyPI with automated changelog generation.
Implementation Strategy
I leveraged modern development practices with comprehensive testing using pytest, automated quality checks with flake8 and mypy, and semantic versioning. The pipeline caught integration issues early and reduced manual overhead significantly.
Leveraging Large Language Models
My experience highlighted the importance of choosing the right AI tool. Initially using Claude Sonnet 3.5, I encountered over-engineering and inconsistent results. Switching to Claude Sonnet 4 in VS Code transformed the experience with precise execution and better context understanding.
Rather than random suggestions, I used structured prompts like: “Create a NetBox API client class with connection pooling, automatic retry logic with exponential backoff, proper SSL certificate handling, and comprehensive error handling for device and VM queries.”
The LLM excelled at boilerplate elimination, API integration patterns, test coverage generation, and maintaining consistent code patterns. I treated it as a sophisticated pair programmer where architecture decisions remained human-driven while leveraging AI efficiency for implementation details.
This collaboration increased development velocity by approximately 40% while maintaining code quality. The key was keeping human judgment central to design decisions while using AI as an advanced autocomplete tool for consistent implementation patterns.
The result is a robust tool that addresses real infrastructure management challenges through methodical development and strategic AI assistance.
For more detailed technical information about the development process, AI collaboration strategies, and implementation specifics, see the complete article.